Azure is the public cloud from Microsoft and was also known as Windows Azure or colloquially Windows Cloud. So in this public platform’s earlier times, there were only “Windows Servers” available to be deployed. At March 2009, Microsoft announced Azure SQL Database as an additional service which customer could deploy.
According to Wikipedia this was the official timeline of Microsofts public cloud (an excerpt):
- October 2008 – Announced the Windows Azure Platform
- March 2009 – Announced SQL Azure Relational Database
- November 2009 – Updated Windows Azure CTP, Enabled full trust, PHP, Java, CDN CTP, and more
- February 2010 – Windows Platform commercially available
- December 2011 – Traffic manager, SQL reporting, HPC scheduler
- June 2012 – Websites, Virtual machines for Windows and Linux, Python SDK, the new portal, locally redundant storage
- April 2014 – renaming of Windows Azure to Microsoft Azure, and introducing ARM Portal at Build 2014.
- July 2014 – Machine Learning public preview
- October 2018 – Microsoft joins the Linux-oriented group Open Invention Network.
More in detail…
Microsoft announces several new services and features throughout the whole year, so it is challenging to name all of those services here, but I think I’ll try to introduce you to a lot of those services and features within this blog. Some in general and some of them with more insight, description, and demonstration of those functioning.
Actually, Microsoft has too many services to name them all, and giving you an overview would take very long, so let me show you a big overview picture.
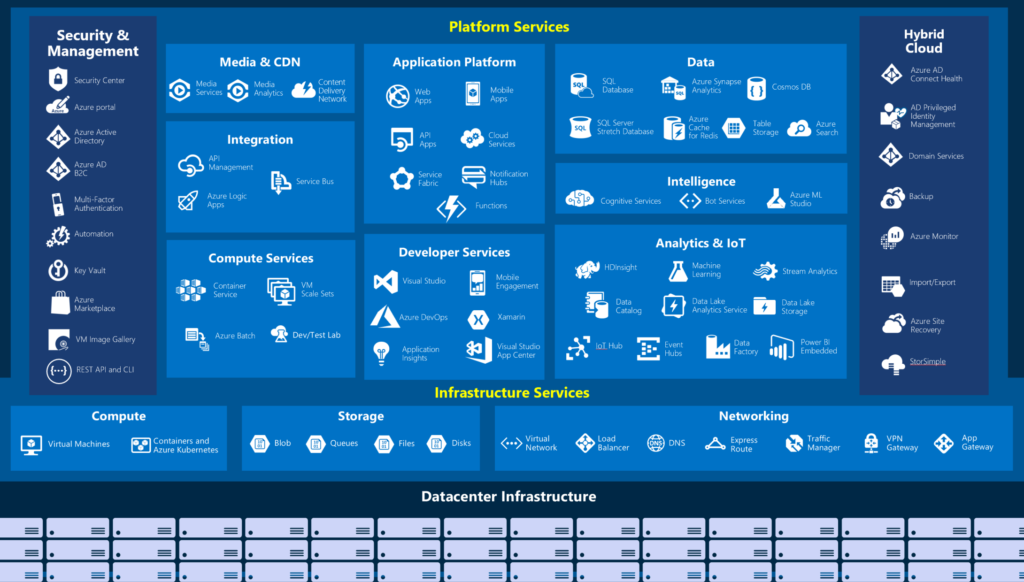
As you can see from the picture, there are many different services over a lot of different categories for a kind of workload. So you can realize a lot of scenarios for all of your software solutions and application no matter what base it is building. You can deploy a “simple” virtual machine with an SQL Single database that might be filled up by API-calls operated by web-functions. And of course, you can gain insights with several monitoring and alerting functionalities and options like Monitor or Log Analytics. Microsoft will enhance all those services on a regular base not only bug fixes, but a lot of enhancements, new features, new performance level, and nearly all services with a high SLA of 99,9%
I will try to describe many of those solutions and opportunities in each blog post, some more on a basic level, some with more insights and demos.

